With their high hardness, wear resistance, and precision characteristics, tungsten carbide balls are indispensable components in precision instruments. Advances in their manufacturing processes and expanding application areas will further drive the development of related industries.
1. Characteristics of Tungsten Carbide Balls
High Hardness and Wear Resistance: With hardness approaching that of diamond, tungsten carbide balls withstand intense friction and wear, ideal for long-term operation in precision components.
High Strength and Compressive Resistance: Their compressive strength exceeds 6000 MPa, suitable for high-load environments.
Corrosion Resistance: Tungsten carbide balls exhibit excellent resistance to acids, alkalis, and other chemicals, making them suitable for harsh working conditions.
High Precision: Through precision machining, they achieve G5–G10 accuracy levels with minimal diameter tolerances and high surface finish, meeting the stringent requirements of precision instruments.
High-Temperature Stability: They maintain stable performance in high-temperature environments, suitable for precision equipment operating under elevated temperatures.
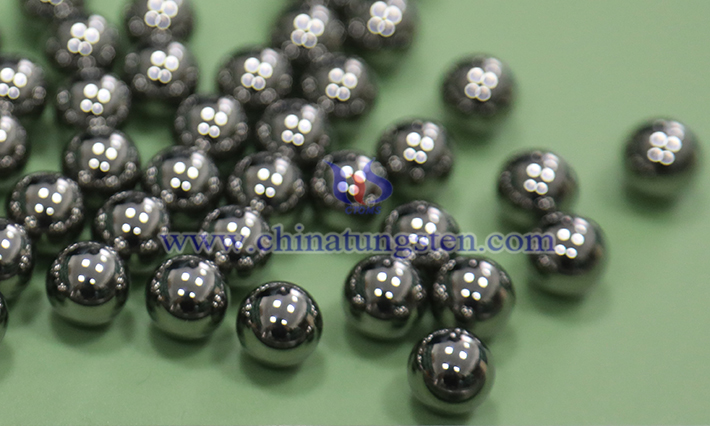

2. Manufacturing Process of Tungsten Carbide Balls
Raw Material Preparation: Tungsten carbide powder is mixed with cobalt powder in precise proportions, with trace additives to optimize performance.
Press Forming: The mixed powder is pressed into spherical blanks using high-precision molds.
Sintering: High-temperature sintering in a vacuum or hydrogen-protected furnace densifies the blanks, forming a high-strength structure.
Precision Grinding and Polishing: Multiple grinding processes ensure the balls achieve high precision and a smooth surface.
Quality Inspection: Optical measuring instruments, roundness testers, and other equipment are used to verify the balls’ dimensions, roundness, and surface quality, ensuring compliance with standards.
3. Application Areas of Tungsten Carbide Balls in Precision Instruments
Precision Bearings: Used as rolling elements in high-speed, high-precision bearings to reduce friction and improve operational efficiency, such as in aerospace equipment and high-speed machine tools.
Measuring Instruments: In coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) and probe systems, tungsten carbide balls serve as probe tips, ensuring high-precision measurements.
Valves and Seals: In high-pressure valves and fluid control systems, tungsten carbide balls function as sealing balls, offering corrosion resistance and superior sealing performance.
Optical Instruments: In laser equipment and optical alignment systems, tungsten carbide balls are used for precision positioning.