CTIA GROUP LTD tungsten resin is a composite material made from tungsten powder and a resin matrix (such as polyethylene, epoxy resin, or other polymer materials), widely used in radiation shielding, fishing gear, and biomimetic materials. The preparation methods for tungsten resin vary depending on the matrix type, tungsten powder content, and application requirements, with common techniques including injection molding, compression molding, press-sintering, and high-speed mixing-calendering.
1. Injection Molding
Injection molding is suitable for preparing flexible composite materials with high tungsten content, commonly used for products not requiring sintering, such as fishing gear or flexible shielding materials. This method involves mixing tungsten powder with a modified resin matrix and molding, offering a simple process with no need for additional finishing.
Preparation Steps:
Mixing: Combine tungsten powder with a resin matrix (typically polyethylene-based) and additives (e.g., plasticizers, dispersants, stabilizers) in a closed mixing device at an appropriate temperature to ensure uniform mixing and full encapsulation of tungsten particles by the resin.
Injection Molding: Inject the mixture into a molding machine and shape it under suitable temperature and pressure.
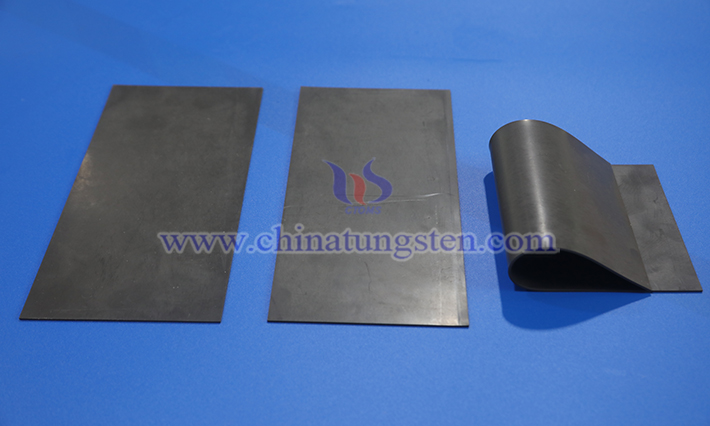
2. Compression Molding
Compression molding is often used to produce radiation shielding materials, such as tungsten/epoxy resin composite panels, suitable for nuclear protection applications. This method employs radiation-resistant resin matrices and micron-sized tungsten powder to ensure both shielding performance and mechanical strength.
Preparation Steps:
Matrix Selection and Pre-treatment: Choose a resin with excellent radiation resistance and test its stability in radiation environments.
Mixing: Blend tungsten powder, resin, curing agents, and dispersants evenly to prevent tungsten powder agglomeration.
Compression Molding: Pour the mixture into a mold and cure it under appropriate pressure and temperature, then demold the finished product.
Post-processing: Conduct performance tests as needed, such as shielding effectiveness or mechanical property assessments.
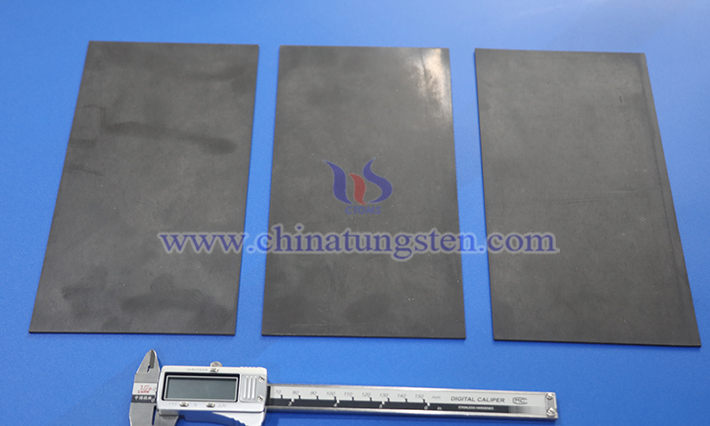

3. Press-Sintering
Press-sintering is suitable for flexible tungsten resins with lower tungsten content, using polymer compounds as binders, with the finished product offering some deformability.
Preparation Steps:
Mixing: Thoroughly mix tungsten powder with a polymer binder to ensure uniform distribution.
Pressing: Compress the mixture into a shaped blank under high pressure.
Sintering: Heat the material to cure and form it, resulting in a smooth surface with some flexibility.
4. High-Speed Mixing-Calendering
High-speed mixing-calendering is used to produce radiation shielding panels, typically with PVC or rubber as the matrix, creating flexible or semi-rigid composite materials.
Preparation Steps:
High-Speed Mixing: Rapidly stir tungsten powder, resin matrix, and additives (e.g., stabilizers, plasticizers) at high temperature to ensure a uniform mixture.
Gelation: Allow the resin raw material to fully gel, forming a homogeneous mixture.
Filtration: Remove impurities to ensure material purity.
Calendering: Process the mixture into sheets or panels using calendering equipment.
Cooling and Setting: Cool the product to achieve the final shape.
The preparation of tungsten resin requires attention to tungsten powder particle size (typically micron-sized for optimal dispersibility), compatibility between resin and tungsten powder, and environmental friendliness. The choice of process should be flexibly adjusted based on application needs (e.g., flexibility, shielding performance, or mechanical strength).



