As an advanced composite material, tungsten resin is increasingly valued in the nuclear industry. This material combines the unique properties of tungsten with the flexibility of resin, forming an efficient and reliable solution suitable for nuclear environments requiring high protection and durability.
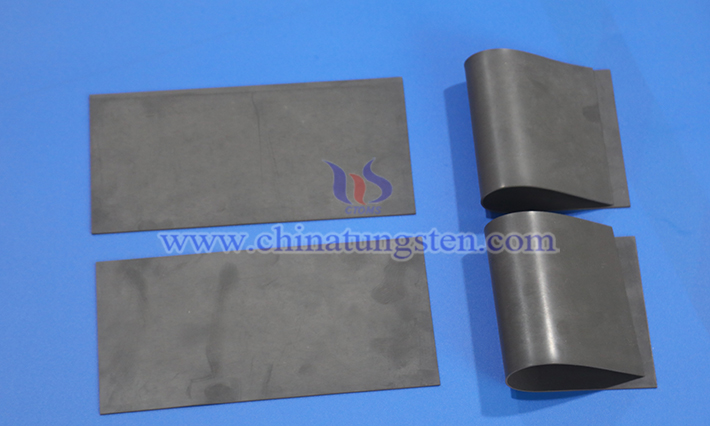
In radiation shielding, tungsten resin plays a central role. The nuclear industry involves significant radiation exposure, such as rays generated during reactor operations, fuel processing, and waste management. Tungsten resin is manufactured into shielding panels, containers, or casings to block harmful radiation, protecting workers and equipment. It is well-suited for use in nuclear power plant shielding walls or isolation zones, effectively absorbing and attenuating radiation to ensure a safe operating environment. Compared to traditional shielding materials, tungsten resin is easier to process into complex shapes, allowing it to fit closely to equipment surfaces and reduce the likelihood of radiation leakage.
Tungsten resin is also commonly used in support structures or fixed components inside reactors, which must remain stable under high temperatures and radiation. The resin matrix provides flexibility and vibration resistance, while the tungsten component enhances heat resistance and protective capabilities.
In the field of nuclear waste processing and storage, tungsten resin applications are equally significant. The nuclear industry generates large amounts of radioactive waste, requiring safe storage and transportation containers. Tungsten resin is used as the outer layer or lining of waste canisters, effectively shielding radiation emitted by the waste and preventing environmental pollution. Its moldability allows manufacturers to customize container shapes based on waste types, ensuring sealing and durability. During transportation, tungsten resin containers can withstand vibrations and impacts, reducing leakage risks. Additionally, in nuclear decommissioning projects, it serves as a temporary shielding tool during the dismantling of old reactors, assisting workers in safely handling residual radiation. This application not only improves waste management efficiency but also meets the nuclear industry's environmental requirements by avoiding secondary pollution from traditional materials.
Tungsten resin also extends its use in radiation detection equipment. In nuclear power plant monitoring systems, it is integrated into sensor components to provide real-time radiation monitoring, helping prevent accidents. Its non-magnetic properties and stability make it suitable for use in nuclear facilities with strong magnetic fields, avoiding equipment failures.
Furthermore, tungsten resin plays an increasingly prominent role in nuclear safety protective equipment. Nuclear industry workers require personal protective gear, such as enhanced layers in protective suits or gloves. Tungsten resin can be embedded in these items, providing lightweight radiation shielding that allows greater freedom of movement while maintaining high protection levels. In emergency responses, it is used to quickly construct temporary shielding walls to control radiation spread. The material's biocompatibility and non-toxicity make it an ideal choice, eliminating the risk of exposure to harmful substances.



